Case1: Clinical, radiographic and microscopic features
This is a 49-year-old woman who presented with a non-healing ulcer and mass on the right lateral border of tongue with 1-year duration that was referred to oral pathology clinic (fig1). The patient’s past medical history indicated type II diabetes mellitus and hypertension. He also denied any use of alcohol and cigarettes. On neck examination, there was one palpable lymph node on right side of the neck. An incisional biopsy of the lateral tongue was performed. Microscopic sections showed islands of dysplastic squamous cells with several individual cell keratinization and keratin pearl formation (fig2-4). Ki-67 expression (brown staining) was about 30% (fig5).
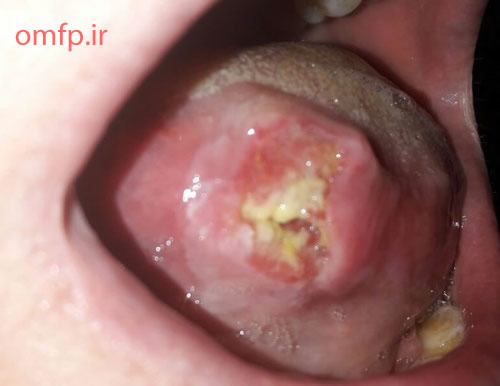
Figure1
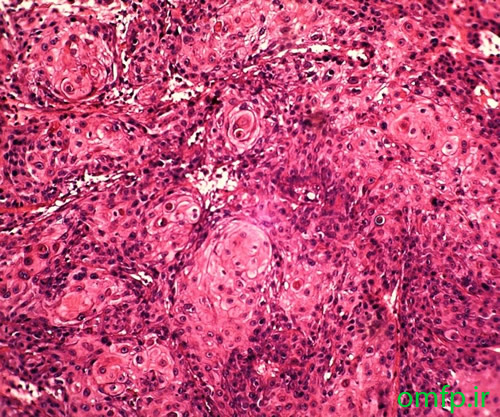
Figure2
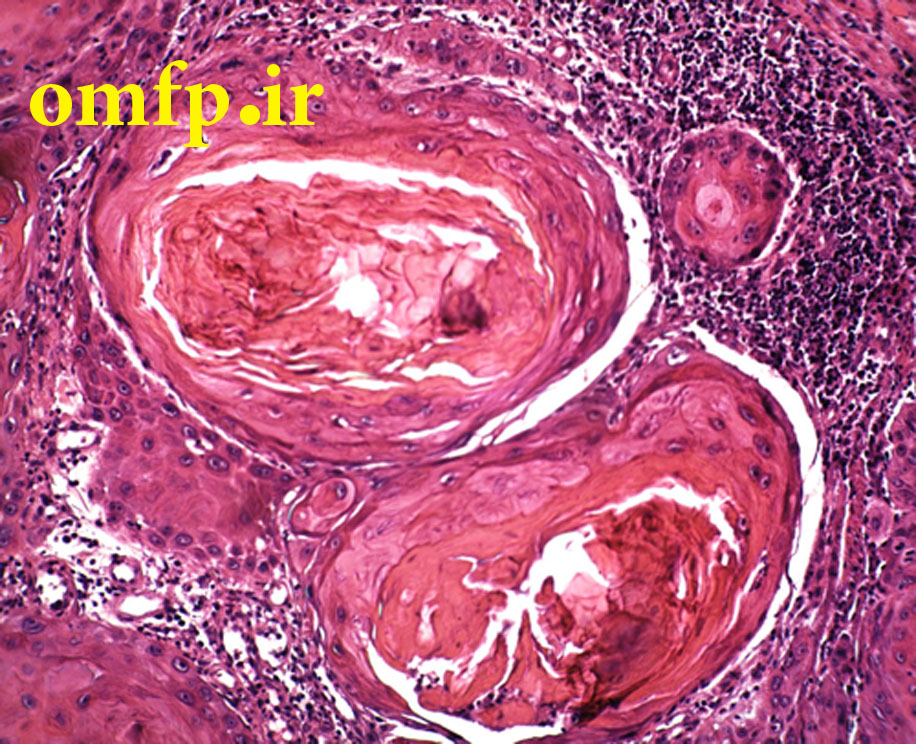
Figure3
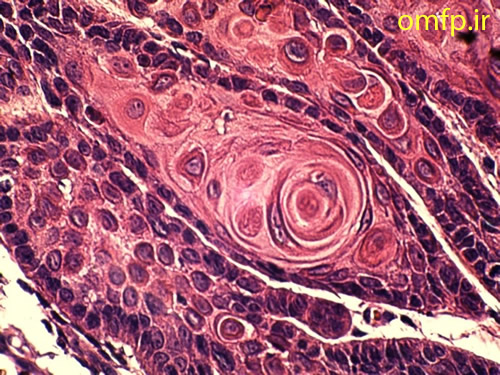
Figure4
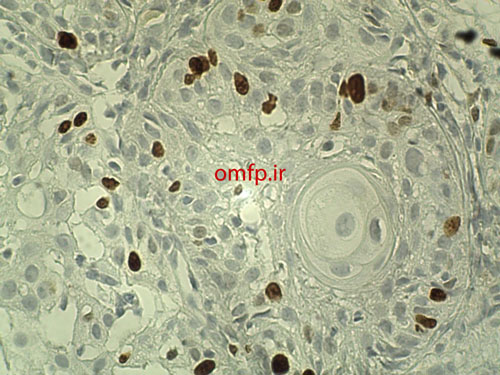
Figure5
تشخیص
Squamous cell carcinoma-SCC
بدلیل اینکه نمونه مورد بحث incisional biopsy می باشد لذا ترجیح بر این است که از اظهار نظر در مورد grading ضایعه خودداری شود ولی اگر نمای excisional biopsy هم به همین صورت بود می توان gradeI (well-differentiated) را برای تومور مطرح کرد. معمولا در تشخیص SCC خوب تمایز یافته نیازی به روش های کمکی مانند IHC نمی باشد. ولی از بررسی Ki-67 برای ارزیابی پرولیفراسیون سلولی و پاسخ به کمورادیوتراپی بعد از جراحی می توان بهره برد.
Case2: Clinical, radiographic and microscopic features
A 56- year-old woman presented with a painless swelling of the anterior of mandible for 2 years duration. The periapical radiograph showed a large multilocular radiolucent lesion that cause anterior tooth displacement (fig1). The aspiration of the lesion showed a serous-like fluid. Incisional biopsy was performed and Gross of the lesion demonstrated solid and creamy cut surface. Histopathologic sections showed a neoplasm composed of nests and islands with ameloblast-like peripheral cells (reverse polarity) and stellate reticulum-like core in the fibrous connective tissue (fig3,4).
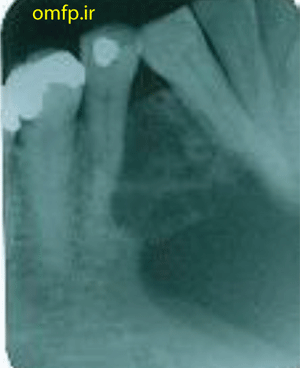
Figure1

Figure2
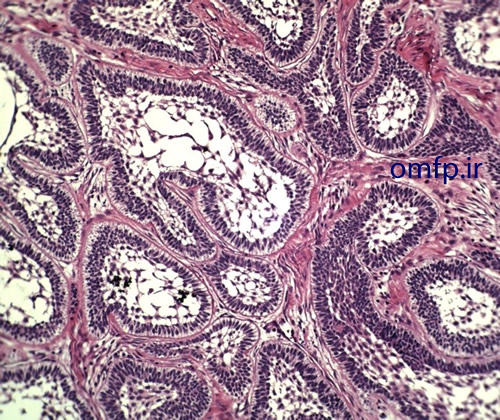
Figure3
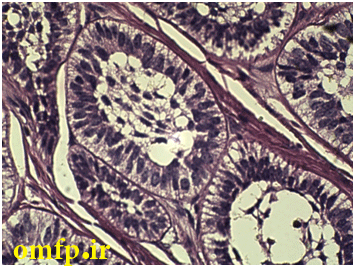
Figure4
تشخیص
Solid ameloblastoma-follicular type
نکات حائز اهمیت این case: در گروس ضایعه و نمای میکروسکوپی بافت تومورال و توپر دیده می شود اما علت مثبت شدن آسپیراسیون چیست؟ آسپیراسیون در ضایعات کیستیک مثبت می شود اما به یاد داریم که در آملوبلاستومای توپر اشاره شده بود که تمایل به ایجاد فضاهای کیستیک متعدد دارد و نام دیگرش (multicystic ameloblastoma) می باشد لذا با اینکه بافت حالت تومورال و توپر دارد اما ممکن است حین انجام آسپیراسیون به داخل یکی از این فضاهای کیستیک بعضا بزرگ وارد شویم. پس مثبت شدن اسپیراسیون، توپر بودن این ضایعه را رد نمی کند. برای افتراق آملوبلاستوما از آملوبلاستیک فیبروما به چند نکته می توان اشاره کرد. بافت همبند در آملوبلاستوما فیبروزه و در آملوبلاستیک فیبروما دنتال پاپیلایی می باشد. در ضمن در آملوبلاستیک فیبروما علاوه بر جزایر، ساختارهای طنابی شکل (cord) حضور دارد که در تشخیص کمک کننده است. این طنابها تمایل به جوانه زدن دارند.
Case3: Clinical, radiographic and microscopic features
A 9-year-old girl presented with a painless swelling of the left mandible for 8 month duration. The panoramic radiograph revealed a well-defined radiolucent lesion surrounded the crown of two premolars (fig1). The excisional biopsy was performed. Microscopic sections showed a cystic lesion lined by nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium (fig2). Small islands of inactive-appearing odontogenic epithelial rests was present in the fibrous wall (fig3). The epithelium and connective tissue interface was flat. Scattered chronic inflammatory cells were also seen in the underlying connective tissue.
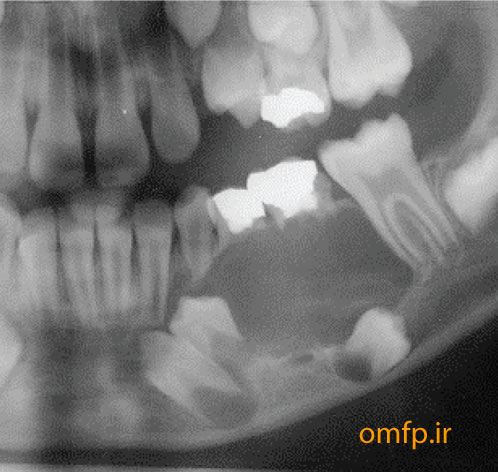
Figure1
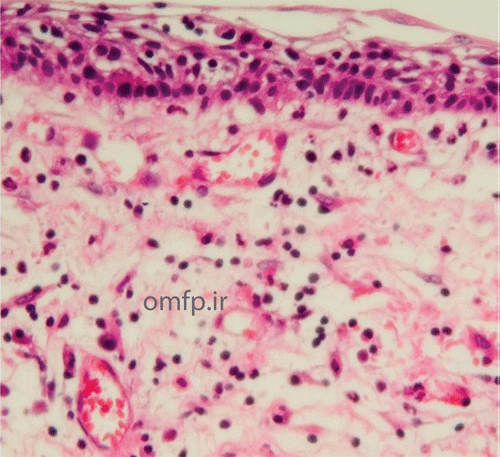
Figure2
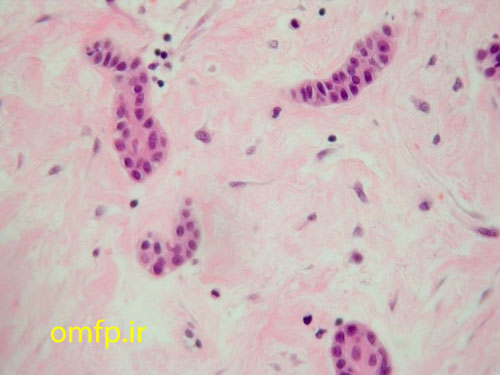
Figure3
تشخیص
Dentigerous (follicular) cyst
Case4: Clinical, radiographic and microscopic features
This is a 70-year-old edentulous man who presented with a painless mass on the floor of the mouth with unknown duration that was referred to oral pathology clinic (figure1). He mentioned episodic pain at mealtime. On panoramic radiograph, there was a large radiopaque mass on the floor of the mouth (figure2). An excisional biopsy was performed. After excision a large brown-yellow mass was appeared (figure3, 4).
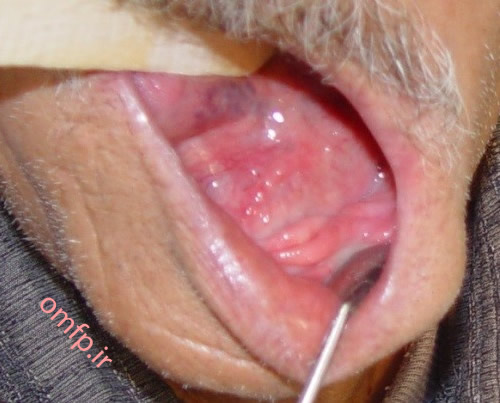
Figure1
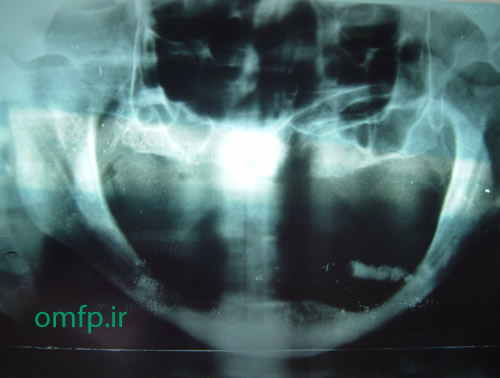
Figure2
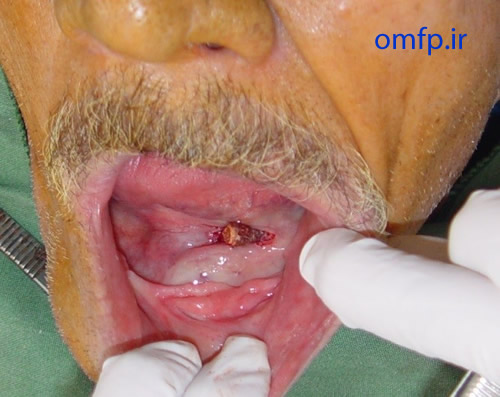
Figure3
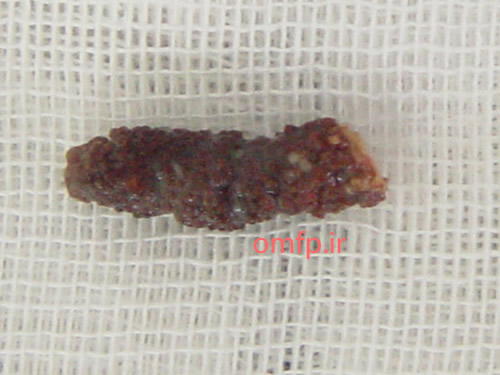
Figure4
تشخیص
Sialolithiasis (salivary calculi-salivary stone) of submandibular gland-warton duct
Case5: Clinical, radiographic and microscopic features
A 24- year-old man presented with a swelling on the left side of face and maxilla with 4-month duration .Enlargement of the upper lip with elevation of the ala of the nose was evident .No pain ,no parasthesia and no lymphadenopathy was seen .Anterior teeth loosening was evident A large swelling with purple color was seen in anterior of maxilla that extended palatally and labially with displacement of the central tooth (figure1) .Radiographic images showed a large radiolucent lesion occupied the anterior of maxilla with root resorption (figure2) .Microscopic sections showed many multinucleated giant cells in a background of ovoid to spindle shaped mesenchymal cells .The stroma was loose .Many RBCs and blood vessels were also seen (figure3).
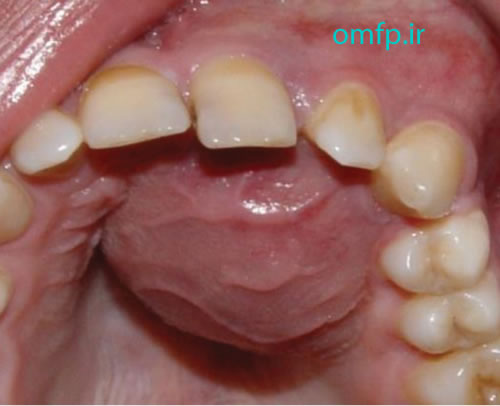
Figure1
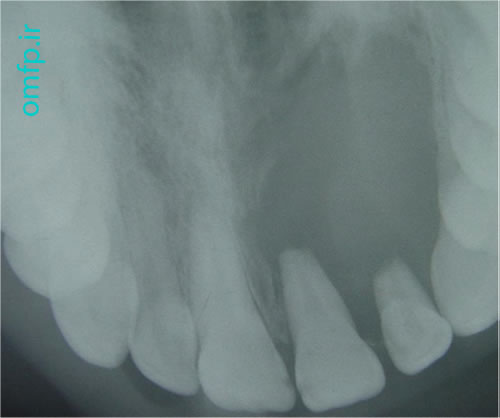
Figure2
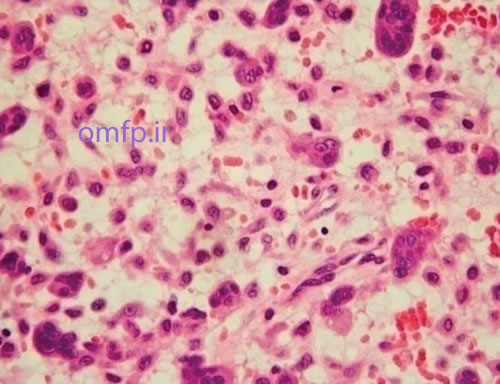
Figure3
تشخیص
Central giant cell granuloma-CGCG
Case6: Clinical, radiographic and microscopic features
A 6 -month-old infant presented with an ulcerated mass of the anterior mandibular gingiva with 1 month duration (figure1) .The lesion had soft consistency .Excisional biopsy was performed. Histopathologic sections showed a diffuse infiltration of large ,pale-staining mononuclear cells that resemble histiocytes intermixed with many eosinophils (figure2, 3) .The lesion covered by fibrinopurulent membrane .IHC for CD1a and S100 were positive.
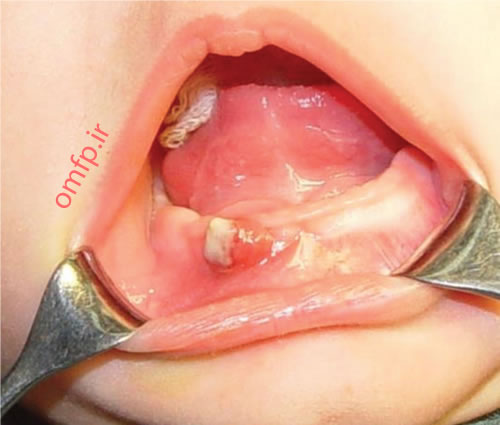
Figure1
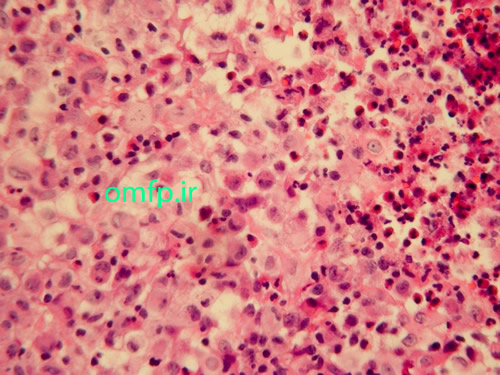
Figure2
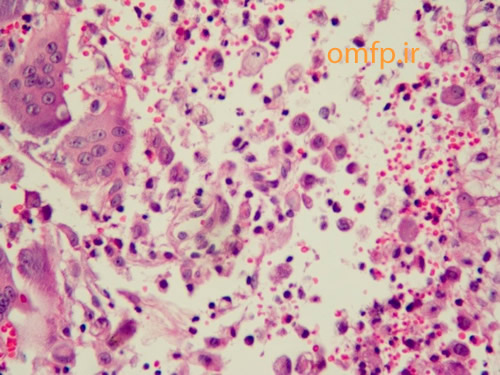
Figure3
Diagnosis
Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCA) or Eosinophilic granuloma
The Histiocyte Society, in order to better define prognostic categories of Langerhans cell histiocytosis, has proposed the following classification:
- Single organ involvement—typically bone or skin
- Unifocal disease
- Multifocal disease
- Multi-organ involvement
- No organ dysfunction
- Organ dysfunction
- Low-risk (skin, bone, lymph nodes, and/or pituitary gland)
- High-risk (lung, liver, spleen, and/or bone marrow)
Case7: Clinical, radiographic and microscopic features
A 50 - year -old man presented with an ulcerated mass of the right mandibular gingiva with 1 year duration (figure1) .He had poor oral hygein .The excisional biopsy was performed. The cut surface of the gross was solid and brown (figure2) Histopathologic sections showed many multinucleated giant cells in a hemorhhagic background of ovoid to spindle shaped mesenchymal cells covered by ulcerated oral mucosa. A zone of dense fibrous connective tissue separated the giant cell proliferation from the mucosal surface (figure3, 4). Some of giant cells had large, vesicular nuclei; others demonstrated small, pyknotic nuclei (figure5, 6).
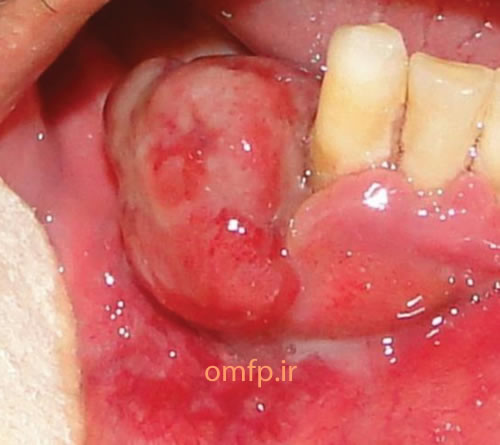
Figure1
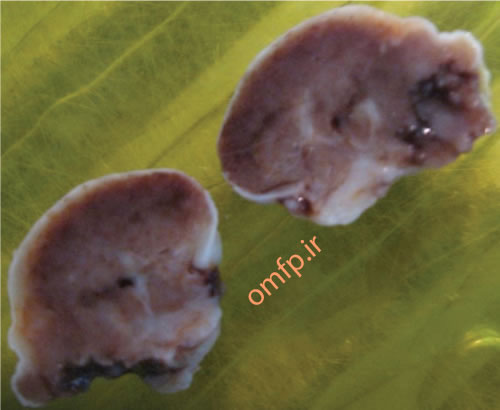
Figure2
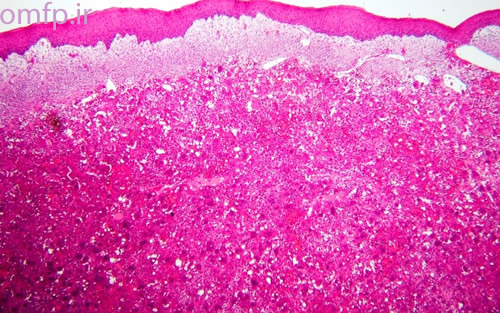
Figure3
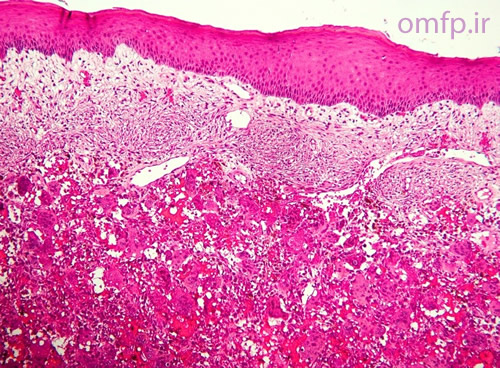
Figure4
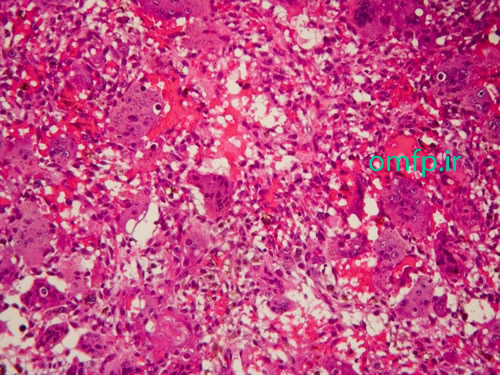
Figure5
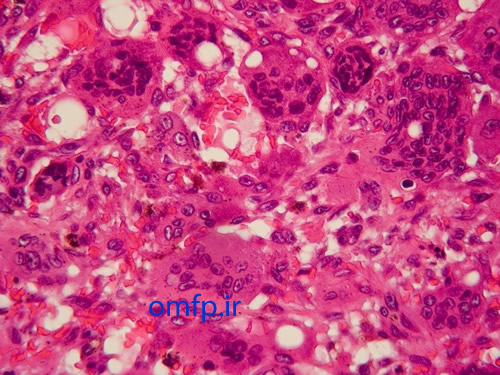
Figure6
تشخیص
Peripheral giant cell granuloma-PGCG
Case8: Clinical and microscopic features
This is a 19-year-old man who presented with a painless non-healing mass on the right lateral border of tongue with 2-month duration that was referred to oral pathology clinic. Intraoral examination showed a large mass on the lateral tongue with white-red irregular surface (Figure1 ,2). On neck examination, there was no evidence of lymphadenophaty. He had no history of smoking, drinking of alcohol and systemic disease. An incisional biopsy of the lateral tongue was performed. Sections showed nests and islands of dysplastic squamous cells with keratin pearl formation (Figure3).
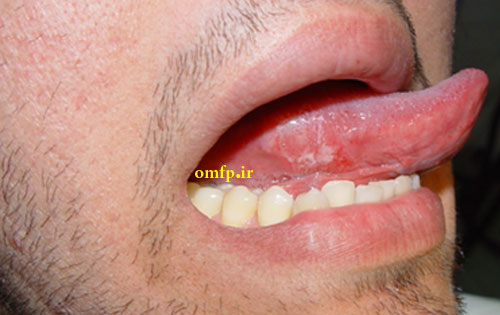
Figure1
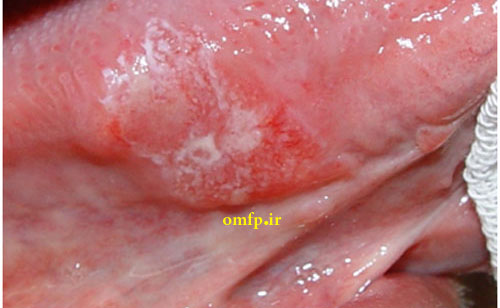
Figure2
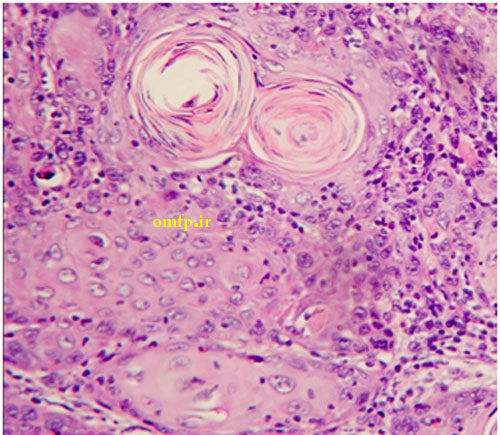
Figure3
Diagnosis
Squamous cell carcinoma
Case9: Clinical and microscopic features
A 25 - year-old woman presented with ulcerated and lobulated red mass on anterior mandibular gingiva with 6 months duration (figure1) .The consistency of the lesion was soft. Excisional biopsy was performed. The cut surface of the gross was solid and creamy with brown spots (figure2). Histopathologic sections showed a vascular proliferation that resembled granulation tissue. A mixed inflammatory cell infiltrate of neutrophils, plasma cells, and lymphocytes was evident. Neutrophils were most prevalent near the ulcerated surface; chronic inflammatory cells were found deeper in the specimen. The surface was ulcerated and replaced by a thick fibrinopurulent membrane (figure3-5).
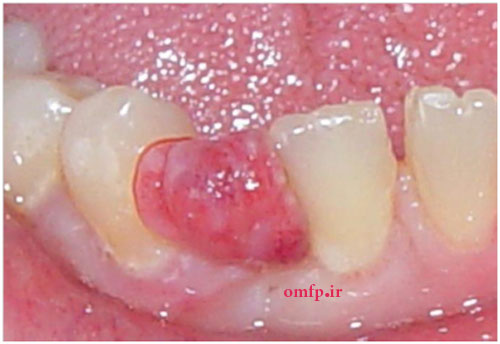
Figure1
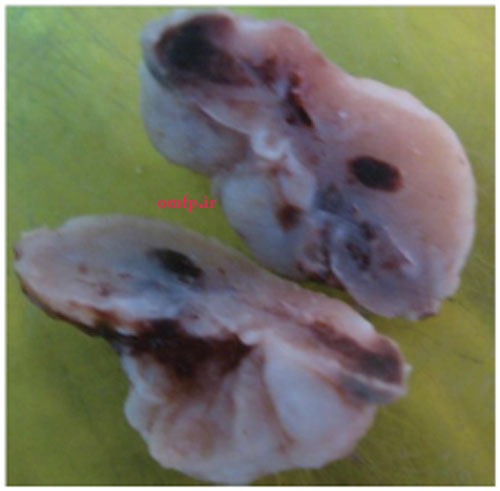
Figure2
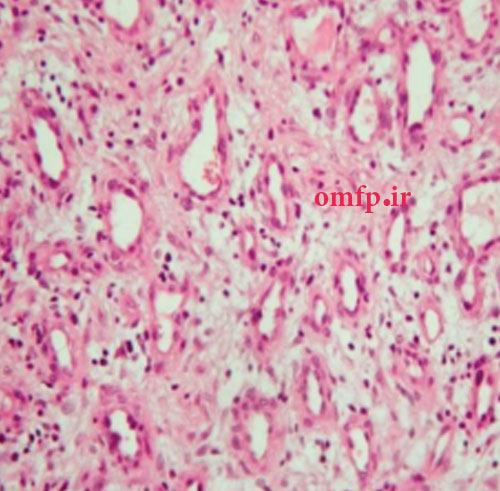
Figure3
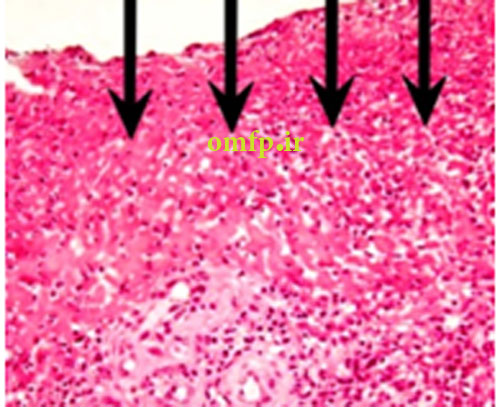
Fig 4. fibrinopurulent membrane
تشخیص
pyogenic Granuloma-PG
Case10: Clinical, Radiographic and histopathologic features
A 37 years old man presented with a large well-defined multilocular radiolucent lesion in the right mandible from second premolar area to the ascending ramus (Figure1). The lesion clinically showed mild expansion. Marsupialization was performed. Microscopic sections showed a cystic lesion lined by parakeratinized stratified squamous epithelium with corrugated surface and palisaded basal layer .Many daughter cysts were also seen in underlying connective tissue (Figure2-4).
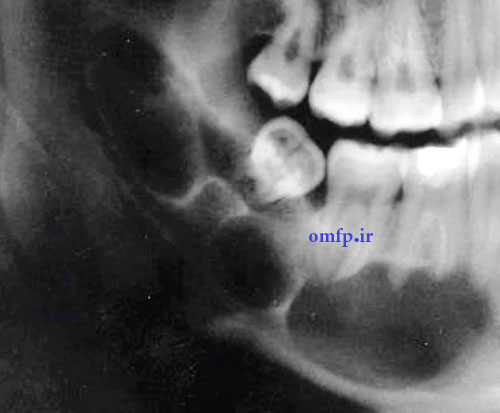
Figure1
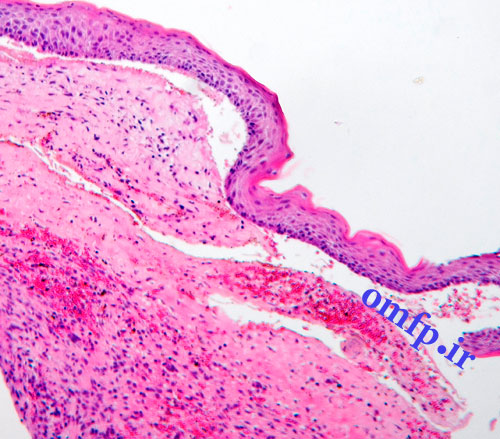
Figure2
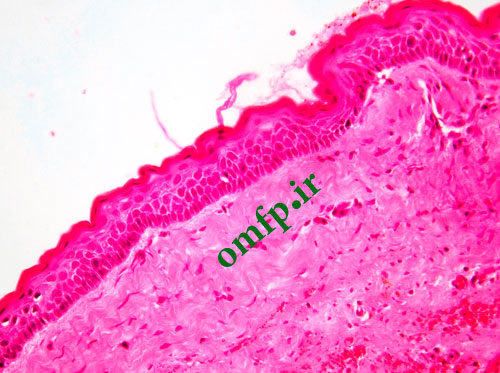
Figure3
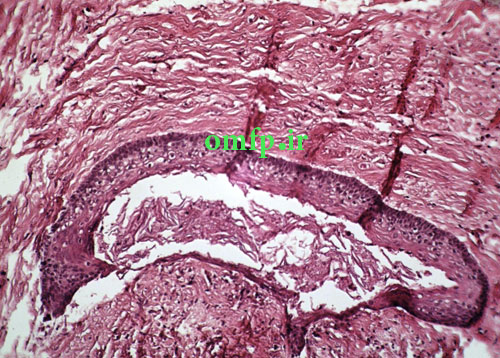
Fig4:Daughter cyst
تشخیص
Odontogenic keratocyst- OKC
Case11: Clinical, Radiographic and histopathologic features
A 13- year-old male presented with a painfull large swelling of the right mandibular area for 6 month duration (figure1). Panoramic radiograph revealed a large radiolucent lesion involved posterior body of mandible and the ascending ramus. Incisional biopsy was performed. Microscopic sections showed a blood-filled spaces surrounded by fibroblastic connective tissue .Scattered multinucleated giant cells were seen adjacent to the spaces. Reactive bone formation was also seen (black arrows) (figure2-4).
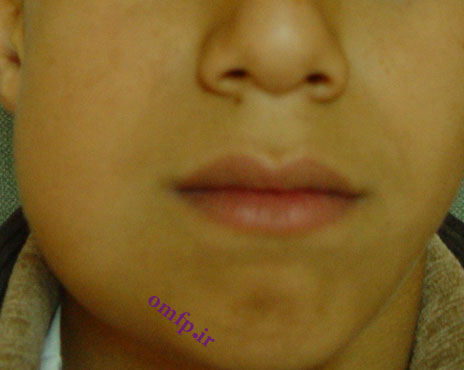
Figure1
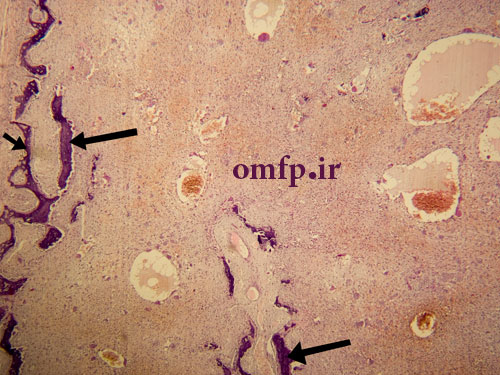
Figure2
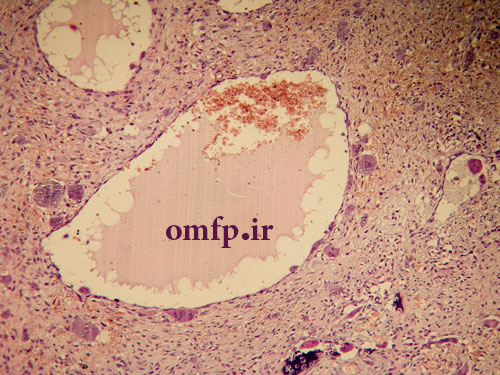
Figure3
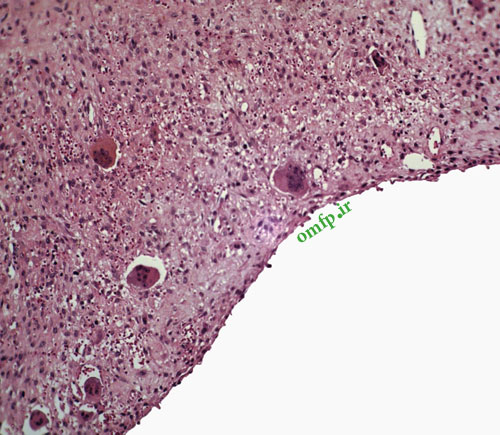
Figure4
تشخیص
Aneurysmal bone cyst- ABC
Case12: Clinical, radiographic and histopathologic features
A 25-year-old female presented with a painless swelling of the left maxilla in molar area for 8 month duration (fig1). The panoramic radiograph revealed a well-defined radiolucent lesion in periapical area of first molar (fig2). The excisional biopsy was performed (fig3) .Microscopic sections showed a cystic lesion lined by nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium (fig4). Underlying fibrous connective tissue demonstrated a chronic inflammatory cells infiltration (lymphocyte-plasmacells), many cholesterol clefts (fig5) and reactive bone formation (fig6).
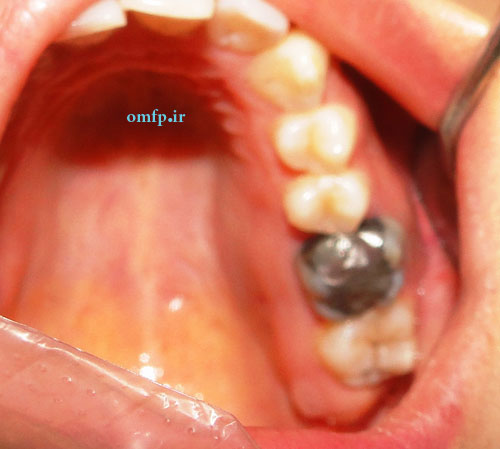
Figure1
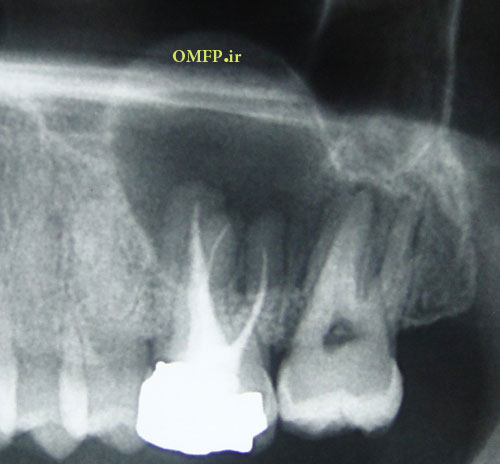
Figure2
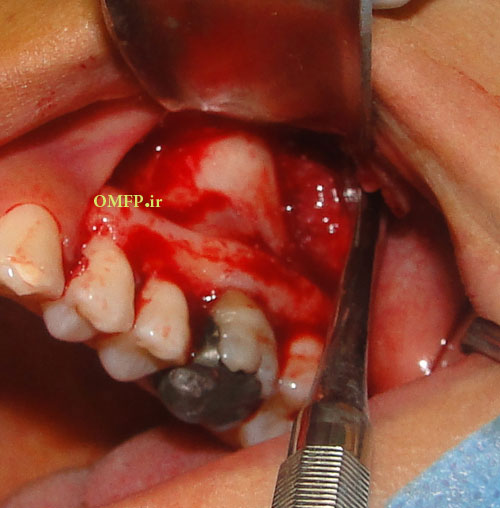
Figure3
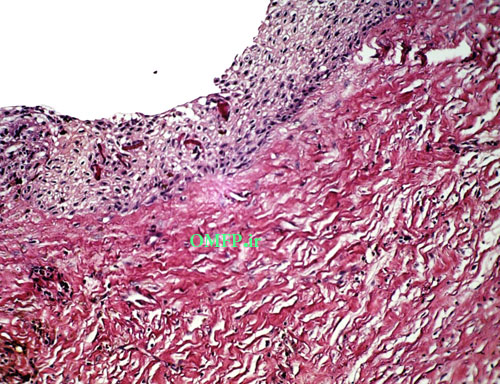
Figure4
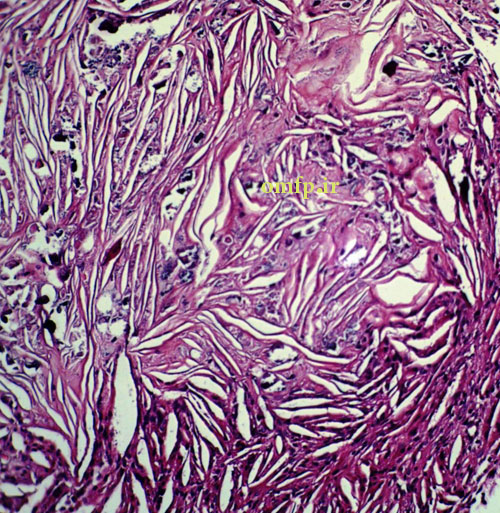
Figure5
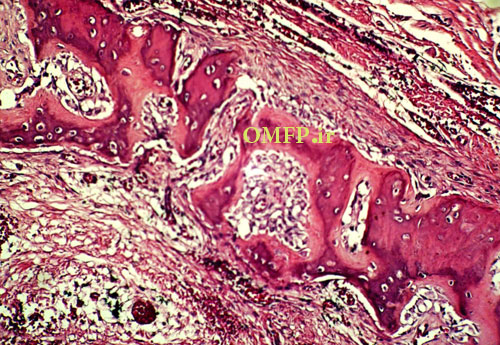
Figure6
تشخیص
Periapical cyst-Radicular cyst
Case13: Clinical and histopathologic features
A 75 - year-old man presented with oral soreness and multifocal large, irregularly shaped ulcerations that existed for at least 6 months (fig1-3).The skin of the back also demonstrated several erosions (fig4). The patient didn’t use angiotensin-converting enzyme [ACE] inhibitors or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs [NSAIDs]. The incisional biopsy was performed and microscopic sections showed an intraepithelial cleft located just above the basal cell layer (fig5). Acantholytic epithelial cells (fig6. Black arrows) were also evident.
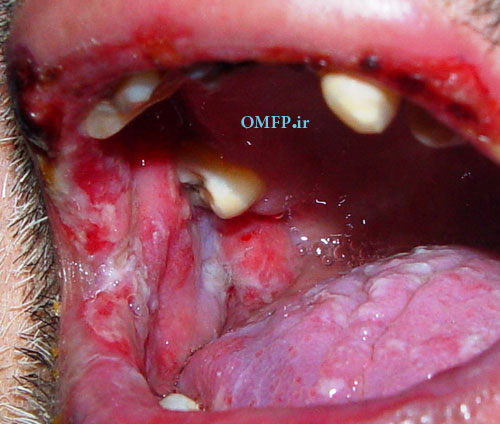
Figure1
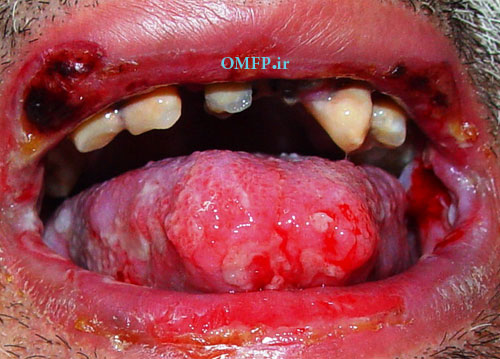
Figure2
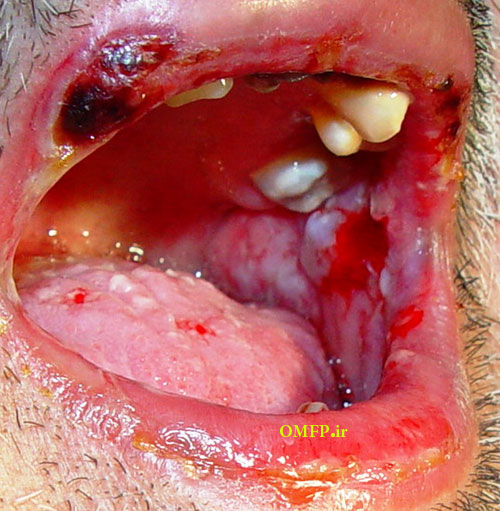
Figure3
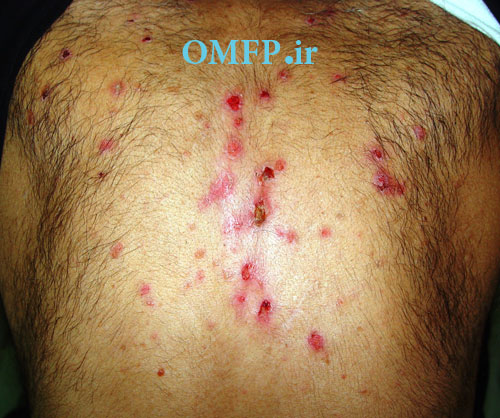
Figure4
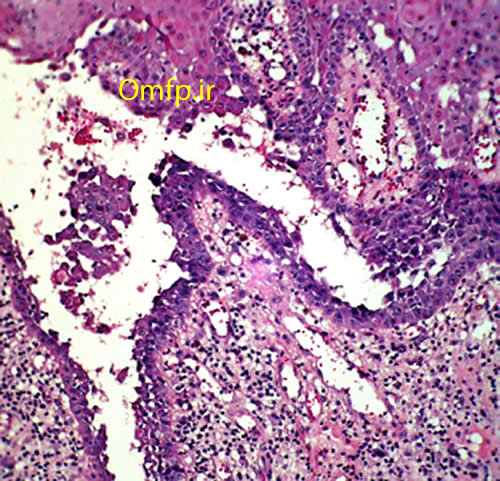
Figure5
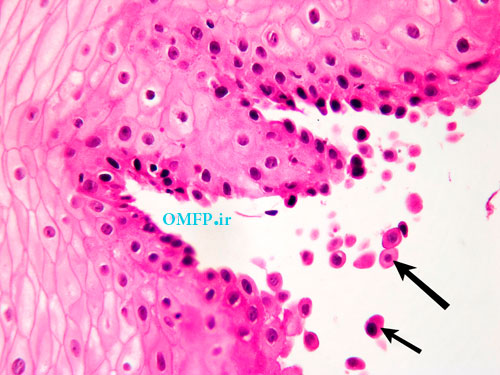
Figure6
تشخیص
Pemphigus vulgaris
Case14: Clinical and histopathologic features
A 40- year-old man presented with folds of hyperplastic tissue in the right maxillary vestibule in association with an ill-fitting maxillary denture (Figures1,2). The lesion completely excised under local anesthesia. The microscopic sections revealed folds of hyperplastic fibrovascular connective tissue covered by stratified squamous epithelium. Infiltration of chronic inflammatory cells are also evident (Figure3,4).
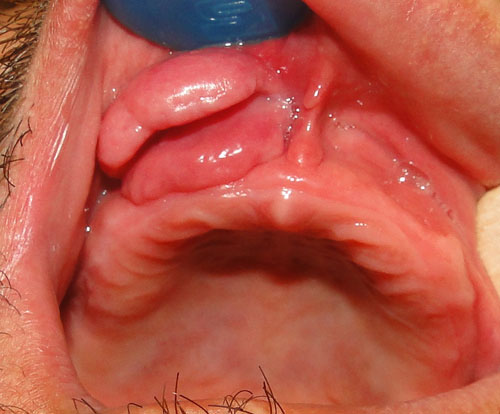
Figure1
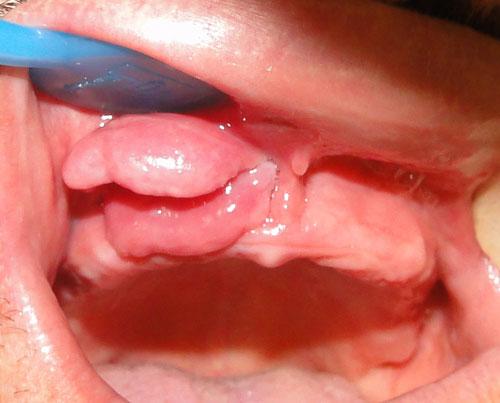
Figure2
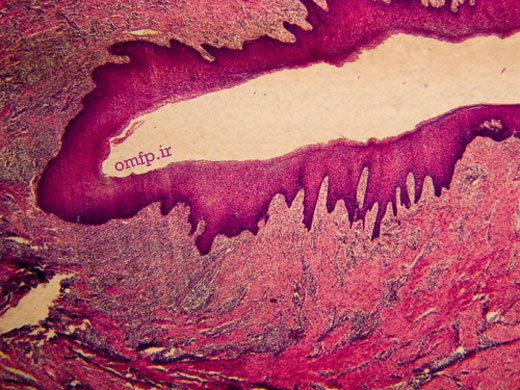
Figure3
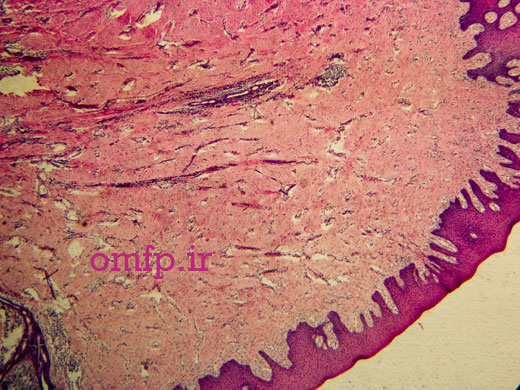
Figure4
تشخیص
Inflammatory fibrous hyperplasia -epulis fissuratum