Case1: Clinical, radiographic and microscopic features
A 79 years old edentulous woman was referred to an oral and maxillofacial pathology center for evaluation of a painless large alveolar mass of right posterior mandible with unknown duration. The lesion was extended toward floor of the mouth and pharynx. The patient’s past medical history indicated use of Zolendronate for osteoporosis for five years. He also denied any use of alcohol and cigarettes. Regional lymphadenopathy was evident on the right side of the neck. An incisional biopsy of mass was performed. In addition there was a mass on left lobe of the lung in CT scan and biopsy was made with CT-guided needle biopsy. Thyroid gland, paranasal sinuses, nasal fossa, larynx and salivary gland tissue were normal in CT scan examination. Oral biopsy showed nests and islands of dysplastic squamous cells with keratin pearl formation (fig1). Lung biopsy showed lung alveolar tissue involved by a malignant neoplasm composed of atypical cells with high N/C ratio and hyperchromatic nuclei arranged in irregular glands (fig2,3). Thus for definite diagnosis IHC for CK7, CK20, CDX2, TTF1, ER, PR and GCDFP15 was recommended. In IHC staining CK7 and TTF1 were positive (fig 4, 5).
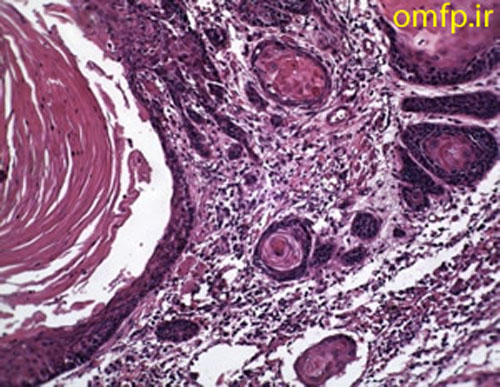
Figure1
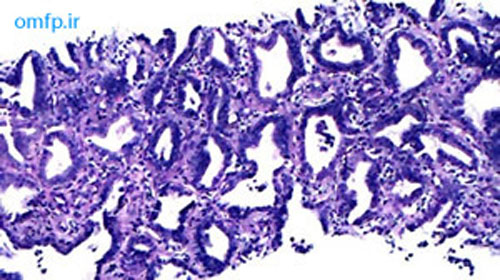
Figure2
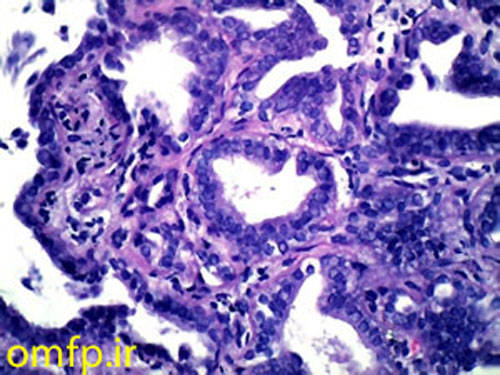
Figure3
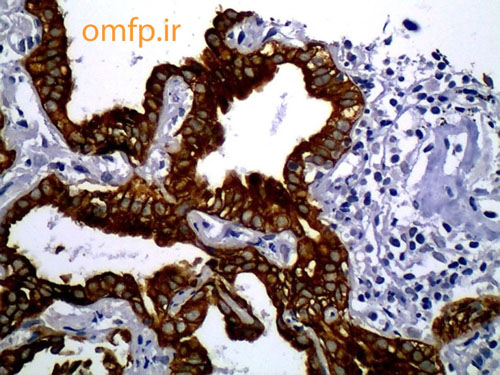
Figure4:CK7
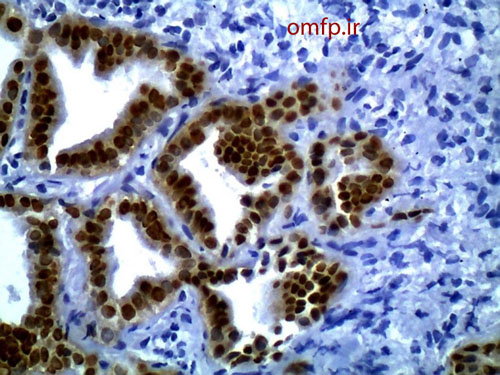
Figure5:TTF1
تشخیص
Synchronous oral squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma with primary lung origin
يکي از علل کاهش بقا در بيماران مبتلا به سرطان هاي سرو گردن به ويژه حفره دهان جدای از پدیده متاستاز، افزايش ريسک ابتلا به يک بدخيمي ثانويه ديگر(secondary primary malignancy [SPM]) می باشد. با بررسی هاي ژنتيکي ثابت شده است که منشا تومورهاي ثانويه با اوليه متفاوت مي باشد و اين تفاوت در منشا موجب بروز مشکلات درمانی می گردد. SPM به دو گروه synchronous(ابتلا همزمان) و metachronous(ابتلا در زمانهای مختلف) تقسیم می شود. ابتلا همزمان وقتی است که فرد در خلال 6 ماه هر دو بدخيمي رانشان دهد و در صورتي که 6 ماه از تشخيص سرطان اوليه گذشته باشد غیر همزمان محسوب می شود. الگوي ابتلا به SPM در جوامع مختلف متفاوت مي باشد مثلا در اروپا بيشتر به صورت بدخيمي ريه و در ژاپن به صورت بدخيمي دستگاه گوارش بروز می یابد. مصرف سيگار و الکل دو ريسک فاکتور اصلي براي ابتلا به SPM مي باشند. در حفره دهان درگيري نواحي تحتاني حفره دهان مانند کف دهان احتمال ابتلا به SPMرا بالاتر مي برد. مطالعات متعدد نشان داده اند که پروگنوز اين بيماران به طور واضحي از بيماراني که فقط يک بدخيمي دارند ضعيفتر است. تمام اين مسائل بيانگر اين نکته است که بيماران مبتلا به سرطان سر و گردن بايد پيگيريهاي دقيق و مدت دار داشته باشند تا در مراحل ابتدايي،SPM مشخص گردد. متاسفانه این بیمار حدود 1 ماه بعد از تشخیص ضایعه فوت نمود. مارکرهای تشخیصی به کار رفته در این بیمار. با بررسی نمای میکروسکوپی نمونه ریه فرضیه متاستازSCC به ریه منتفی شد. لذا از مارکرهای ذکر شده برای منشا تومور استفاده شد. جدول زیر الگوی بروز CK7, CK20 رو در انواع بدخیمی های اپی تلیالی رو مشخص می کند.
- TABLE 1: CK7 & 20 expression in various epithelial malignancies.
- Lung (adeno) CK7+/CK20−
- Lung (SCC) CK7−/CK20−
- Colon CK7−/CK20+
- Breast CK7+/CK20−
- Kidney CK7−/CK20−
- Prostate CK7−/CK20−
Case2: Clinical, radiographic and microscopic features
A 32 years old woman was referred to the Oral Pathology service, with multiple painless maxillary and mandibular gingival masses(fig1-3). The patient had noticed their appearance after extraction of the molar teeth in these areas about 3 months prior to referral. There was no response to antibiotic treatment. On extra-oral examination, facial asymmetry was seen without palpable lymph nodes in the head and neck region. she mentioned recent weight loss of about 7 Kg. She complained of chin numbness of 1 month duration. Intraoral examination revealed gingival growth extending from the mandibular left first premolar region to the ipsilateral retromolar trigone, from the maxillary first premolar region to tuberosity and in the area of right canine and premolar. The masses were soft to firm and the overlying mucosa was slightly edematous and purple in color. A panoramic radiograph revealed bone resorption in these regions and the extraction sites did not show healing(fig4). Her medical and family histories were not contributory. The patient underwent incisional biopsy from the left maxillary and mandibular lesions. Histopathological exam revealed atypical large lymphoid cells with pleomorphism and hyperchromatism arranged in diffuse sheets in a delicate connective tissue. This specimen was positive for LCA and CD20 and negative for bcl-2, bcl-6, CD10, CD138 and CD3.The Ki67 marker was positive in over 90% of the tumoral cells(fig5-8).
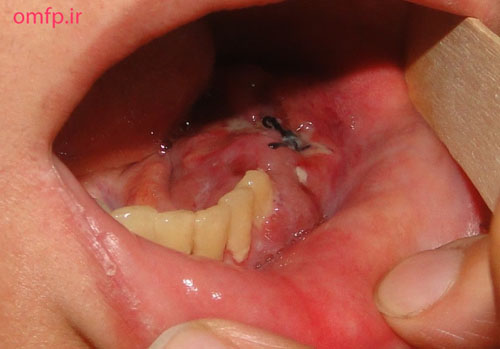
Figure1
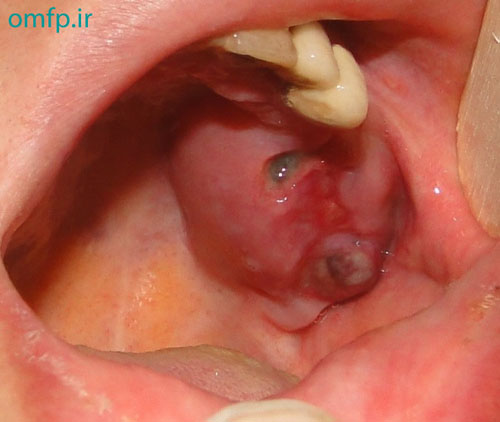
Figure2
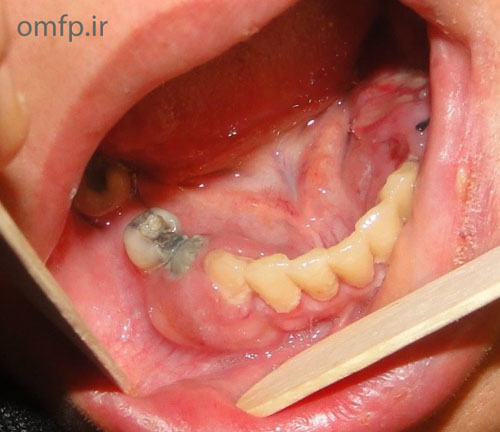
Figure3
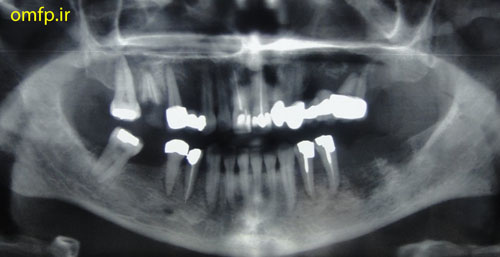
Figure4
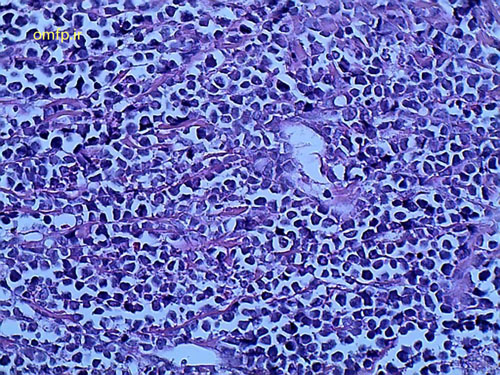
Figure5
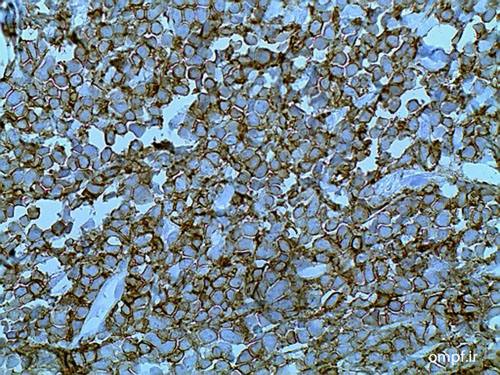
Figure6:LCA
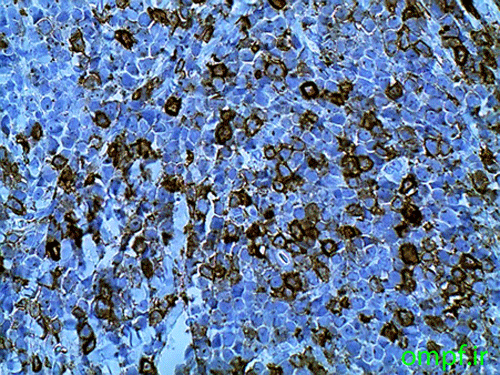
Figure7:CD20
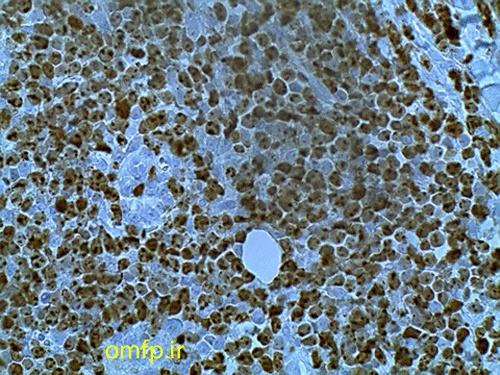
Figure8:Ki-67
تشخیص
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) Subtype Diffuse large B cell lymphoma with very high proliferation activity
NHL ضايعه بدخيمي است كه معمولا غدد لنفاوي را مبتلا مي سازد. ناحيه سر و گردن دومين مكان شايع خارج غده اي بعد از دستگاه گوارش است. اگر ضايعات دهاني چند كانوني در بيماري رويت شد، لنفوم خارج غده اي بايد در تشخیصهاي افتراقي مدنظر قرار گيرد. علائم كلينيكي غير اختصاصي است. لنفوم ها معمولاً به صورت توده زير مخاطي ديده میشوند و برخلاف اسكواموس سل كارسينوم زخم شايع نيست. به دليل شيوع بالاي آبسه هاي دنداني و التهاب، بسياري از دندانپزشكان با ديدن تور مهاي فكي و كامي به سمت اين تشخيص ها می روند و اكثراً اين بيماري در مراحل اوليه به عنوان عفونت هاي ادنتوژنيك تشخيص داده مي شود. لثه و كام مکا لهاي شايع ابتلا مي باشند. یک نکته با اهمیت علامت numb chin می باشد. كارسينوم هاي متاستاتيك پستان و لنفوم ها در بالغين و لوسمي حاد لنفوبلاستيك در كودكان شايع ترين علل ايجاد چانه بي حس مي باشند. لذا بي حسي ناحيه چانه، لب پايين، ناحيه منتال يا لثه بايد اين هشدار را به كلينيسين بدهد كه ممكن است يك بيماري جدي وجود داشته باشد. مارکرهای استفاده شده در این بیمار: مارکر LCAمنشا لنفوسیتی را مشخص می کند. CD138 برای تعیین رده پلاسماسلی کمک کننده است. CD3 نشان دهنده لنفوسیت های T و CD20 نشان دهنده لنفوسیتهای B می باشد. مارکر انتی آپوپتوتیک BCL-2 در لنفوم فولیکولار مثبت می شود. Diffuse large B cell lymphoma بر اساس بروز مارکرهای MUM-1, BCL-6, CD10 به دو زیرگروه Germinal center B cell like (GCB) و Non GCB تقسیم می شود که اهمیت پروگنوستیک دارد. گروه GCB که این مارکرها رو بروز می دهند پیش آگهی بهتری دارند. متاسفانه در این بیمار دو مارکر BCL-6, CD10 منفی بود. بدلیل اینکه درمان در لنفوم ها بر پایه شیمی درمانی می باشد لذا بررسی میزان پرولیفراسیون سلولی که توسط مارکر ki-67 انجام می شود در ارزیابی پاسخ به درمان کمک کننده است. مطالب عنوان شده از کتاب Gnepp و مقاله "لنفوم غير هوچكيني اوليه چند كانوني حفره دهان: گزارش سه مورد به همراه بررسي مقالات" می باشد.
Case3: Clinical, radiographic and microscopic features
A 13-year-old boy with the chief complaint of multiple unerupted teeth was referred to department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery of Ahvaz University of Medical Sciences. The panoramic radiograph revealed 15 unerupted teeth (8 in mandible and 7 in maxilla) with large pericoronal radiolucent zone (enlarged follicles) delineated by a well-defined sclerotic borders (fig1). Tooth abnormalities such as amelogenesis imperfecta were not seen. Medical and familial history was unremarkable and his siblings had normal dentition. The patient had normal intelligence. He did not have other signs and symptoms like cleidocranial dysplasia, Gardner syndrome, or mucopolysaccharidosis. The incisional biopsy was performed with provisional diagnosis of Gorlin syndrome (multiple keratocystic odontogenic tumors). Microscopic examination revealed a dense and cellular fibrous connective tissue with numerous deposits of calcifications. Collagen fibers were arranged in whorled structures. Cords and islands of odontogenic epithelium with numerous clear cells were surrounded by these deposits. Calcifications were found in the whorled areas. There were many small circular droplets of basophilic calcified material resembling cementum (fig 2-4).
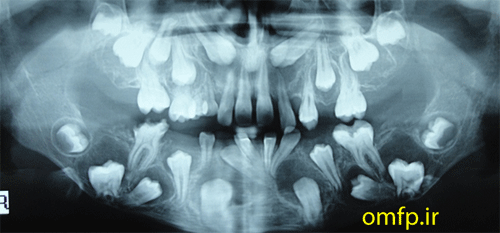
Figure1
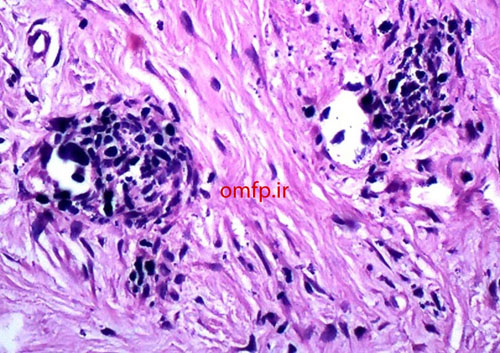
Figure2
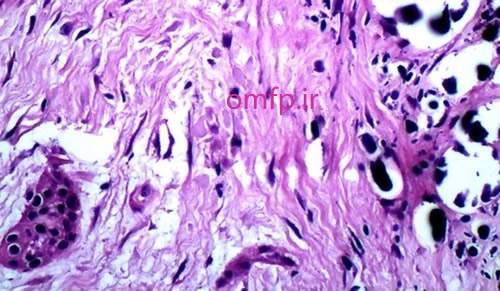
Figure3
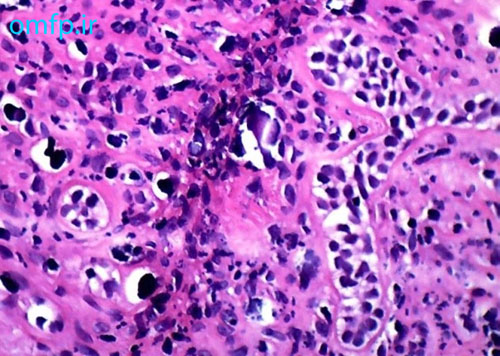
Figure4
تشخیص
Multiple Calcifying Hyperplastic Dental Follicles-MCHDF
تغییرات کیستیک و تومورال ممکن است در فولیکول دندانهای نهفته ایجاد شود. MCHDF یک ضایعه بسیار نادر می باشد که ابتدا به عنوان تغییرات شبه ادنتوژنیک فیبروما در دنتال فولیکول مطرح شد. اتیولوژی آن نامشخص است. Reduced enamel epithelium (REE) که دیواره فیبروزه فولیکول را مفروش می کند در MCHDF دیده نمی شود. تشخیص افتراقی این ضایعه با تومور پیندبورگ و ادنتوژنیک فیبروما مطرح می باشد. هرچند تومور پیندبورگ حاوی مواد آمیلوئید می باشد. و افتراق MCHDF از ادنتوژنیک فیبرومای مرکزی اساسا بر پایه تظاهرات کلینیکی و رادیوگرافی می باشد. درمان ضایعه اکسیژنال بیوپسی می باشد. مطالب برگرفته از مقاله Multiple Calcifying Hyperplastic Dental Follicles: A Case Reportمی باشد.
Case4: microscopic features
A 20 -year-old man presented with a painless sessile nodule on the anterior mandibular gingiva with slight papillary surface measuring 1×1CM .The excisional biopsy was performed. Microscopic sections showed a nodular mass of fibrovascular connective tissue covered by stratified squamous epithelium .Large stellate and giant fibroblasts were seen within the superficial connective tissue (Figure1,2).
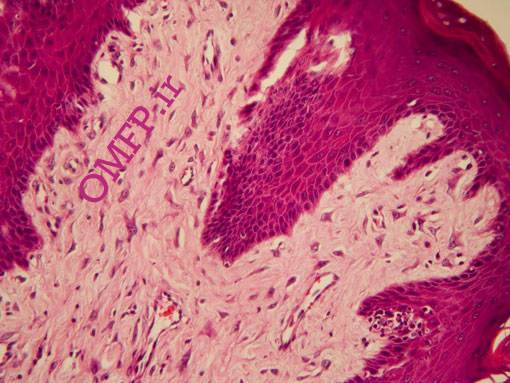
Figure1
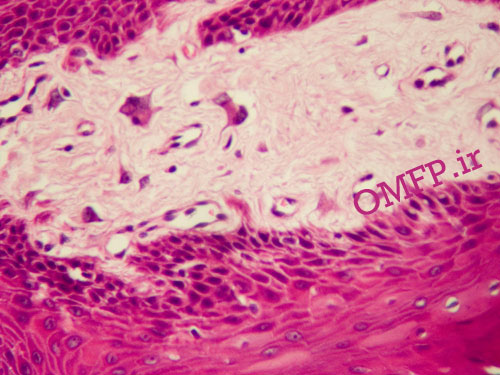
Figure2
تشخیص
Giant cell fibroma
Case5: Clinical and microscopic features
A 58-year-old female was referred to a private oral and maxillofacial pathology center for evaluation of a slowly growing, painless, pedunculated, submucosal mass with a cylindrical shape in the left posterior buccal mucosa. The lesion had about 15 months duration (Figure 1). The nodular mass had soft to elastic consistency measuring 8×4×4mm with an intact overlying mucosa. There was another tiny nonulcerated submucosal mass in the left commissure. There was no history of previous trauma or other medical problems. Both lesions were completely excised with the clinical diagnosis as a reactive or benign neoplastic soft tissue lesion. Microscopic examination of the posterior buccal mucosa showed a well-circumscribed mass with fascicular proliferation of spindle cells showing tendency toward nuclear palisading. The nuclei did not exhibit any pleomorphism or mitotic activity. Apparent verocay bodies were not observed (Figure 2, 3). The immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis for S-100 and GFAP was performed. The lesion cells were strongly positive for S-100 (Figure 4) and negative for GFAP. Lesion of the commissure showed nodular proliferation of fibrous connective tissue. The diagnosis of focal fibrous hyperplasia was made for the buccal lesion. The patient has remained free of tumor for three years postoperatively.
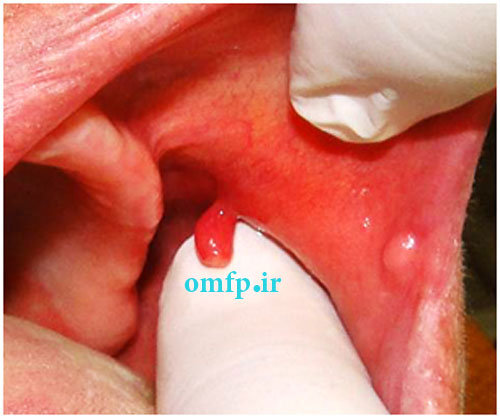
Figure1
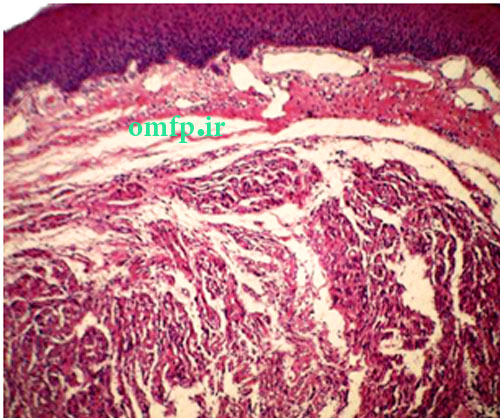
Figure2
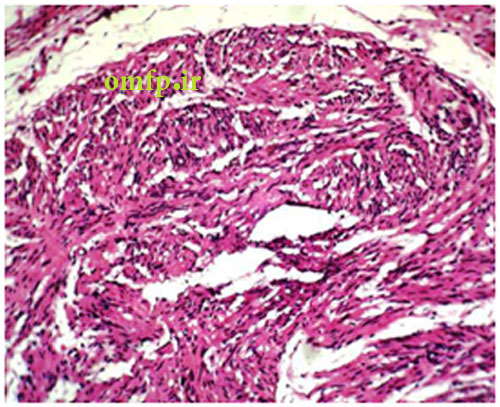
Figure3
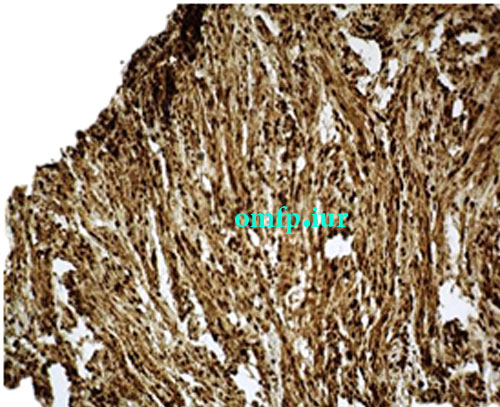
Figure4:S100 expression
تشخیص
Palisaded encapsulated neuroma- Solitary circumscribed neuroma
نکته: برای افتراق palisaded encapsulated neuroma از دیگر تومورهای عصبی مانند شوانوما و نوروفیبروما استفاده از مارکر GFAP کمک کننده است.
Case6: Clinical, radiographic and microscopic features
A 22-year-old man was referred by his dentist for evaluation of the multiple jaw lesions that incidentally was detected in panoramic radiograph. Extra and intraoral clinical examination disclosed no bony expansion or deformity. Panoramic radiograph revealed multiple large, well-defined multilocular radiolucent lesions in the right and left mandibular ramus and from right canine to first mandibular molar. All the lesions had coarse and curved internal septa that cause soap bubble appearance (Figure 1-3). His medical history was noncontributory. The patient underwent incisional biopsy from the left mandibular lesion. Histopathologic evaluation showed scattered multinucleated giant cells in the background of ovoid to spindle mesenchymal cells. Extravasated red blood cells and hemosiderin were also evident (Figure 4). Due to multiple sites involvement and microscopic findings the patient referred to evaluation of paratoromone hormone (PTH) level. The PTH level was 14.5 pg/ml (normal range from 6.5 to 36.8). Calcium and phosphorus inorganic were in normal limit but alkaline phosphatase was slightly elevated probably due to bone destruction. He had no familial history and clinical characteristic of Cherubism, Noonan-like syndrome and neurofibromatosis. Because of asymptomatic lesions, surgical intervention was not performed and the patient was under follow up.
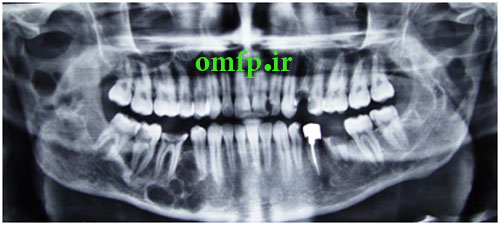
Figure1
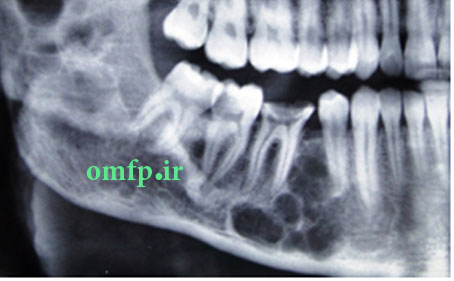
Figure2
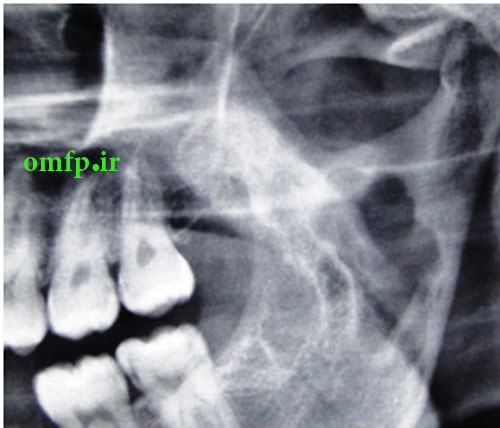
Figure3
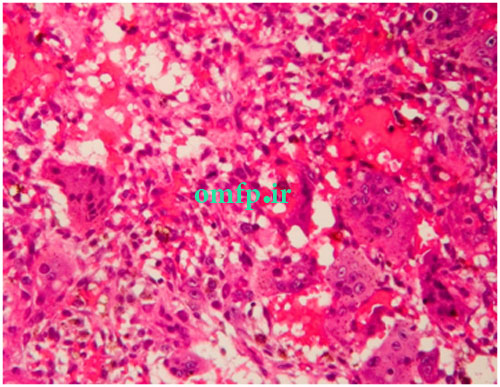
Figure4
تشخیص
Idiopathic multiple central giant cell granuloma
اکثر موارد CGCG به صورت یونی فوکال می باشد و موارد مولتی فوکال معمولا با بیماری سیتمیک زمینه ای مانند هایپرپاراتیروئیدیسم و یا سندرم هایی از قبیل چروبیسم، Noonan-like و Ramon در ارتباط است. در ضمن مواردی از همراهی نوروفیبروماتوزیس تیپ یک و CGCG گزارش شده است. در این بیمار هیچ کدام از موارد فوق دیده نشد. لذا این مورد یاداور می شود که مواردی از CGCG متعدد می تواند به صورت ایدیوپاتیک وجود داشته باشد.
Case7:Clinical, Radiographic and histopathologic features
A 67 years old woman was admitted for evaluation of a painful swelling in the right side of mandible with a 9‑month history. On panoramic radiographic examination, a large ill‑defined radiolucent lesion extending from condyle to symphysis was seen [Figure 1]. Computed tomography (CT) sections presented a destructive soft tissue lesion involving the posterior region of mandible and ramus. There was no regional lymphadenopathy and CT scan of abdomen, pelvic sonography and chest Xray were normal. Based on clinical presentation and radiographic features, a malignant odontogenic tumor like ameloblastic carcinoma, osteosarcoma and central mucoepidermoid carcinoma were considered as the differential diagnoses. Incisional biopsy was performed. Microscopic examination revealed a malignant mesenchymal tumor that was composed of spindle cell proliferation forming rough bundles and fascicles with interlacing pattern. No tumoral necrosis was observed. Spindle cells had blunt‑ended, oval, centrally located nuclei and abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm [Figure 2, 3]. Immunohistochemical analysis for desmin, SMA, S100, myogenin and CK was done. The cytoplasm of tumor cells was positive only for SMA [Figure 4] and desmin [Figure 5]. After diagnosis, hemimandibulectomy was performed under general anesthesia.
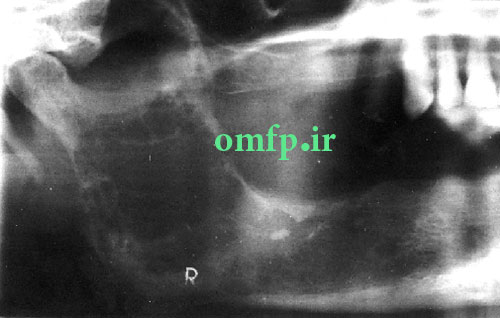
Figure1
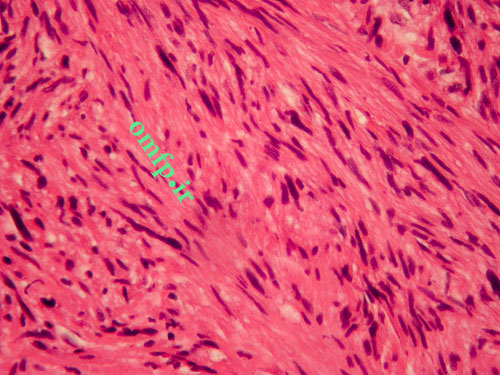
Figure2
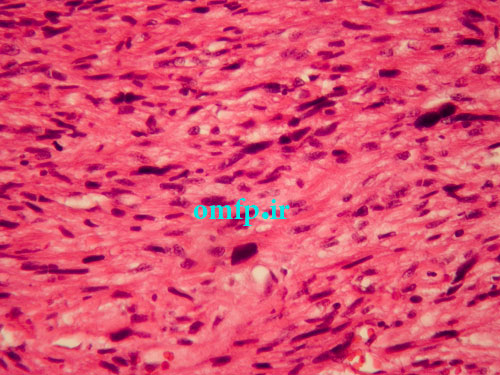
Figure3
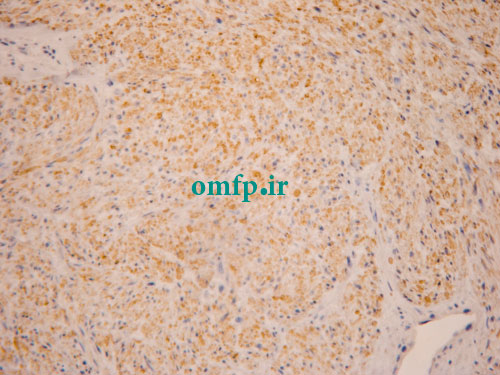
Figure4
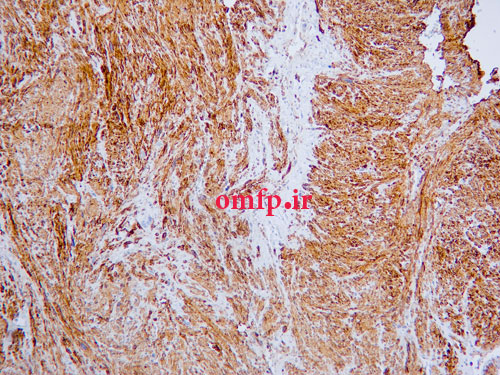
Figure5
تشخیص
Intraosseous leiomyosarcoma
Case8: Clinical and histopathologic features
A 34 years old woman presented with dyspnea, dry cough, fever and chest pain for 3 months duration. She complained of a painless submucosal mass in the left buccal mucosa .The incisional biopsy from oral lesion was performed. Microscopic sections revealed a granulomatous inflammation with collections of histiocytes ,lymphocytes and multinucleated giant cells (figure1, 2) .The granulomas contained laminated basophilic calcification (Schaumann bodies) (figure3).
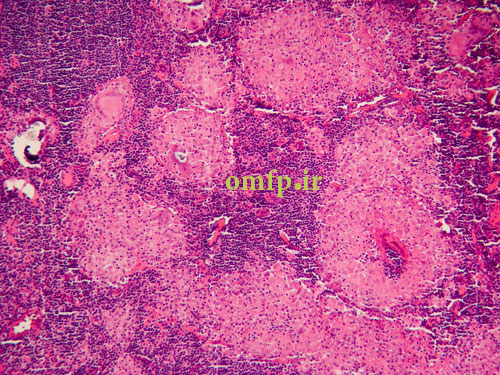
Figure1
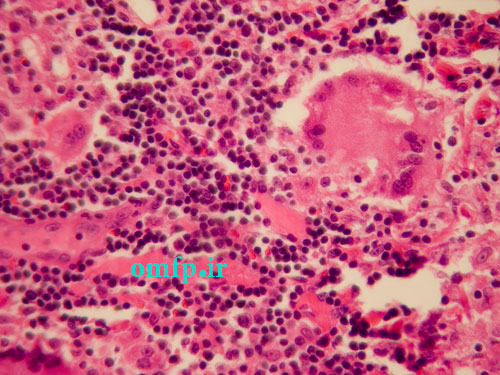
Figure2
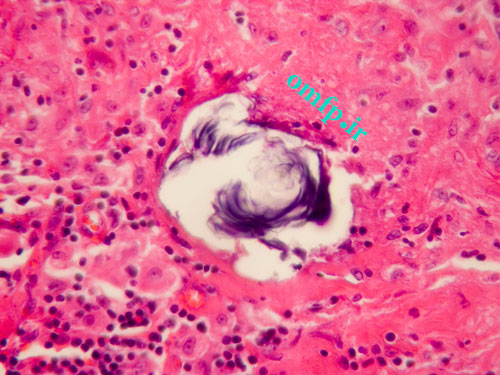
Figure3
تشخیص
Sarcoidosis
Case9: Clinical, Radiographic and histopathologic features
A 65 years old man presented with a large painless mass of parotid for1 -year duration. He had pleomorhic adenoma of parotid gland 30 years ago that treated surgically (figure1, 2). The incisional biopsy was performed. Microscopic sections showed a neoplasm composed of large pleomorphic epithelial cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm. Comedonecrosis within ducts, Roman bridge formation, and an intraductal cribriform pattern were also seen (figure3, 4).
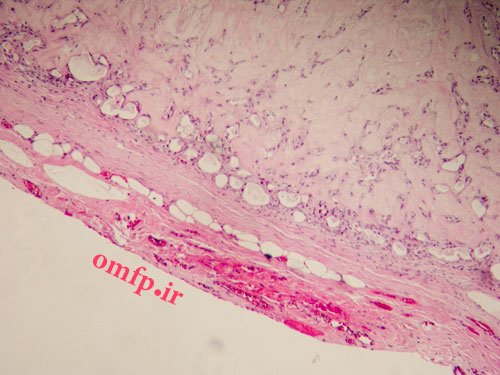
Figure1
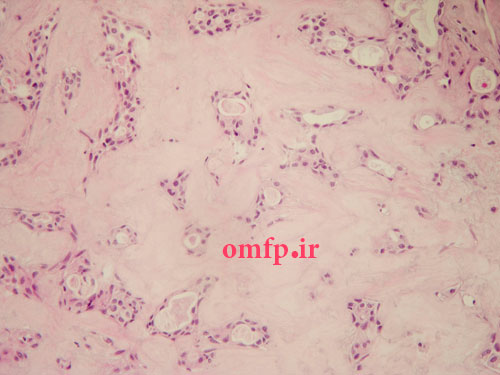
Figure2
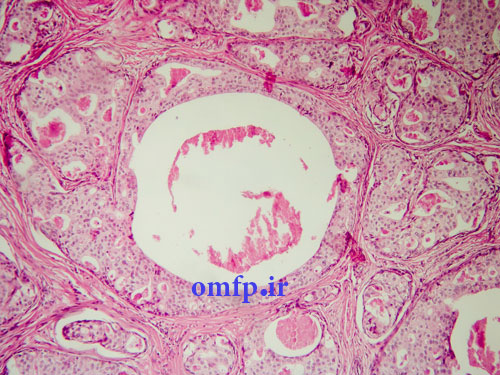
Figure3
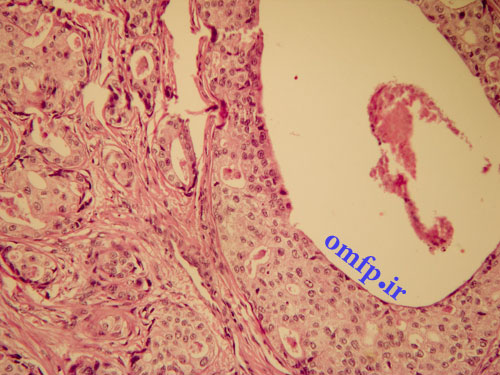
Figure4:S100 expression
تشخیص
Salivary duct carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma
Case10:Clinical, radiographic and histopathologic features
A 25 -year-old man presented with a painless swelling of the left mandible .panoramic radiograph, showed a large, well-defined, radiolucent lesion with scalloping superior border aspect of the lesion between the roots of the teeth (fig 1). The patient mentioned a history of trauma 2 years ago .The biopsy was performed .The gross of the lesion contained fibrous and hemorrhagic tissue (fig 2). Microscopic sections demonstrated a myxofibromatous proliferation intermixed with bony trabeculae , many RBCs ,scattered inflammatory cells , cholesterol clefts and associated giant cells (fig 3-5).
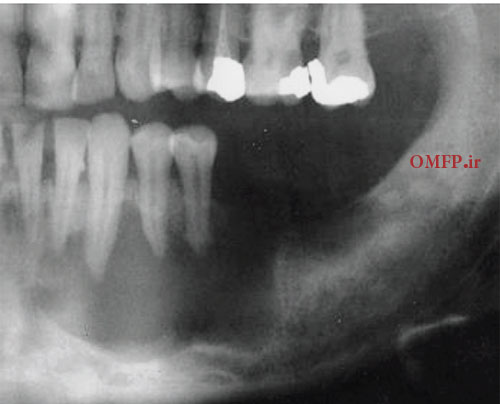
Figure1
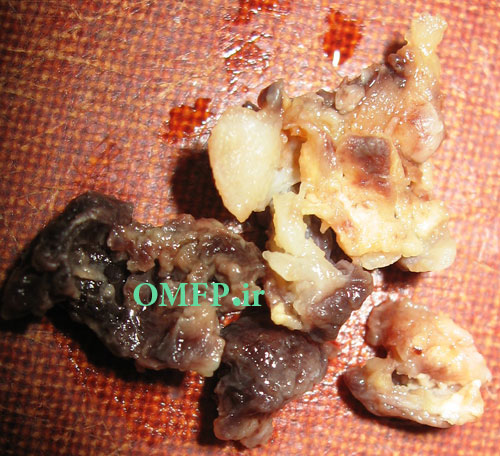
Figure2
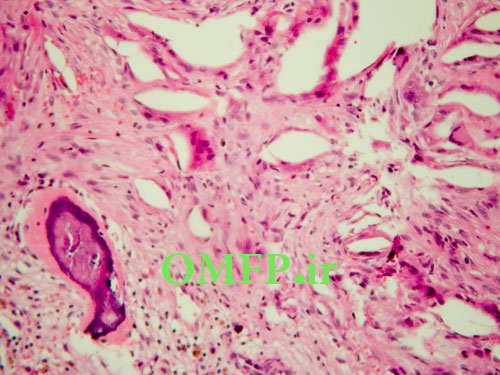
Figure3
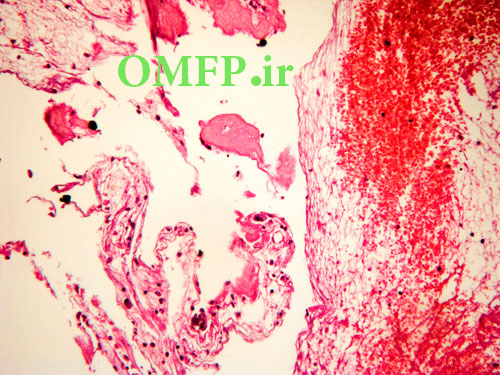
Figure4
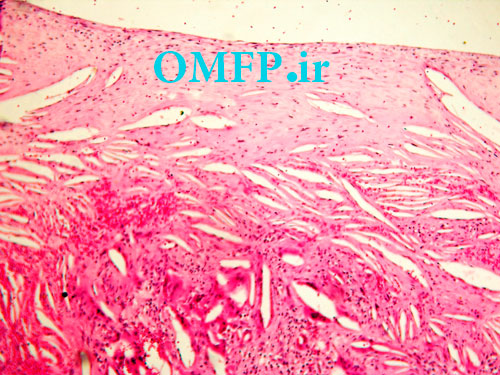
Figure5
تشخیص
Simple bone cyst- solitary bone cyst-unicameral bone cyst
Case11: Clinical, and histopathologic features
A 50 -year-old man presented with a swelling of the left parotid with1 year duration. The microscopic sections revealed multinodular growth patterns .A biphasic tumor with islands , large nests ,or sheets of clear cells composed of scattered small duct lumina lined with two layers of cells was obvious (fig 1-3).
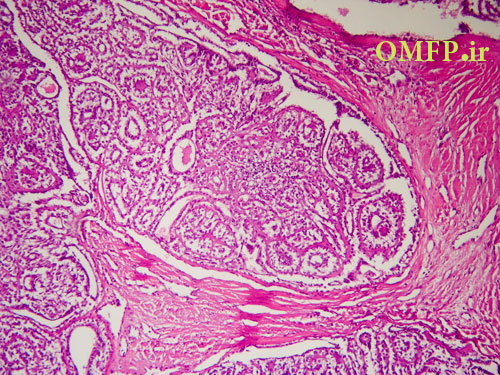
Figure1
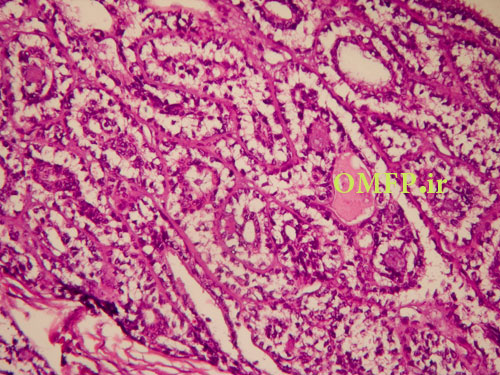
Figure2
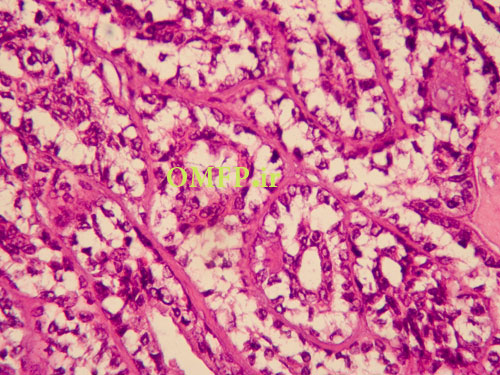
Figure3
تشخیص
Epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma